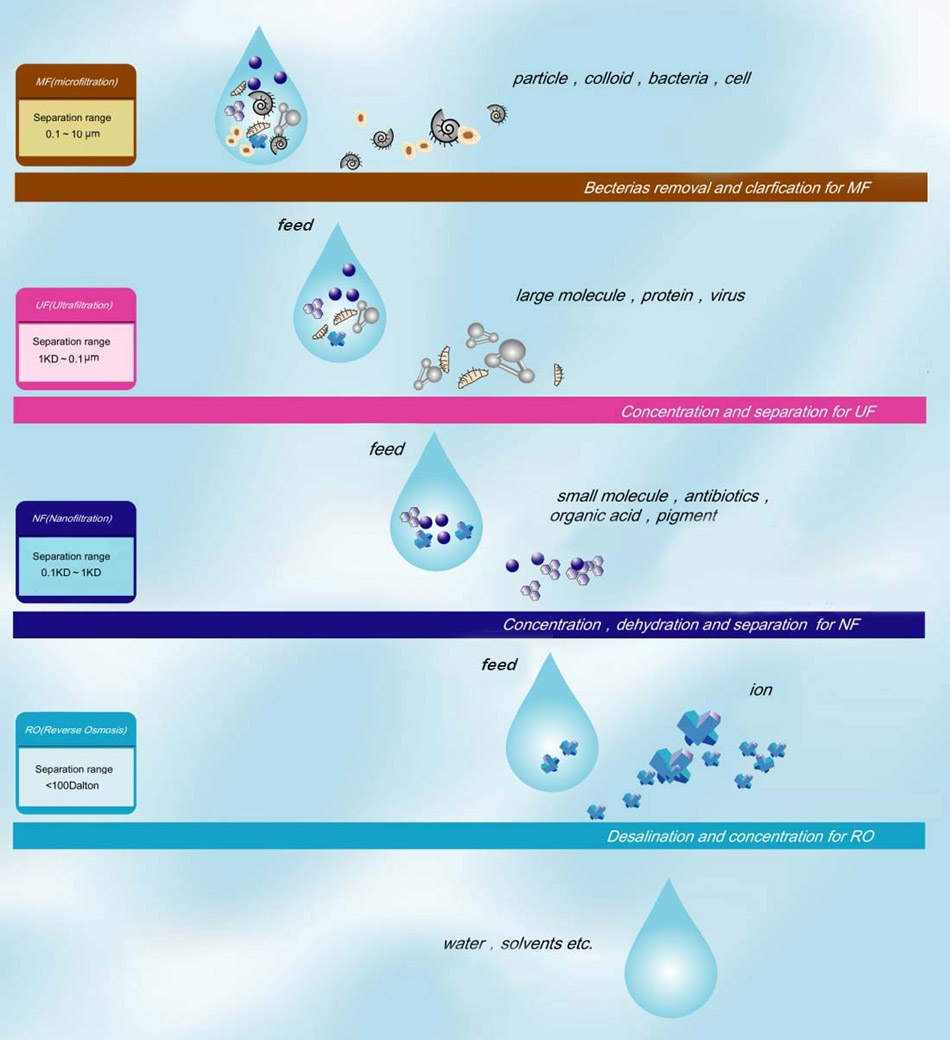
Microfiltration (commonly abbreviated to MF) is a type of physical filtration process where a contaminated fluid is passed through a special pore-sized membrane to separate microorganisms and suspended particles from process liquid. MF membrane is commonly used in conjunction with various other separation processes such as ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis to provide a product stream which is free of undesired contaminants.
Microfiltration membranes(MF)can trap particles between 0.1 and 1 micron. MF allow macromolecules and soluble solids (inorganic salts) to pass through, but will trap suspended solids, bacteria, and high molecular weight colloids. The main industrial application of MF is to
1) remove bacteria and other particles in water;
2) remove bacteria in various solutions such as interstitial fluid, antibiotics, serum, and plasma proteins;
3) remove suspended solids, microorganisms and odor impurities in foods such as beverages, alcohol, soy sauce and vinegar.
MF usually serves as a pre-treatment for other
ceramic membrane separation processes such as ultrafiltration, and a post-treatment for granular media filtration. The typical particle size used for microfiltration ranges from about 0.1 to 10 µm.In terms of approximate molecular weight these membranes can separate macromolecules of molecular weights generally less than 100,000 g/mol.
Applications range of microfiltration (MF) membrane technology
-
Remove suspended solid and reduce SS
-
Remove proteins, polysaccharides, pigments and other impurities
-
Remove bacterial
-
Dehydration
-
Concentration
-
Reduce COD/BOD
Click here for more details about JIUWU
ceramic microfiltration membrane.







 +86-25-58849045
+86-25-58849045
 +86-25-58749295
+86-25-58749295
 jiuwu@jiuwu.com
jiuwu@jiuwu.com
 No. 9 Park Road, Pukou District, Nanjing City (Sanqiao Factory)
No. 9 Park Road, Pukou District, Nanjing City (Sanqiao Factory) Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  No. 9 Park Road, Pukou District, Nanjing City (Sanqiao Factory)
No. 9 Park Road, Pukou District, Nanjing City (Sanqiao Factory)

 English
English 한국어
한국어 français
français русский
русский Español
Español

