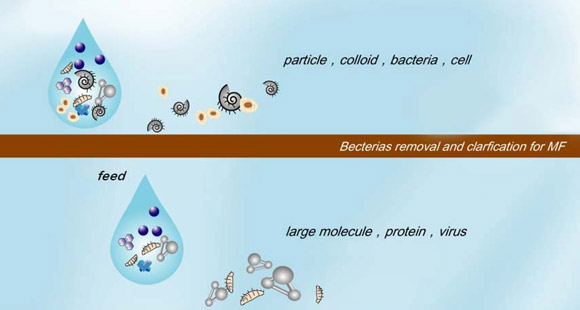
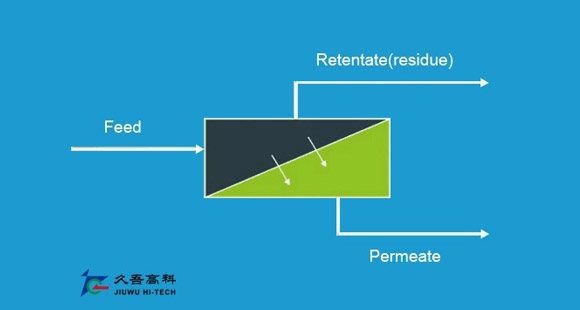
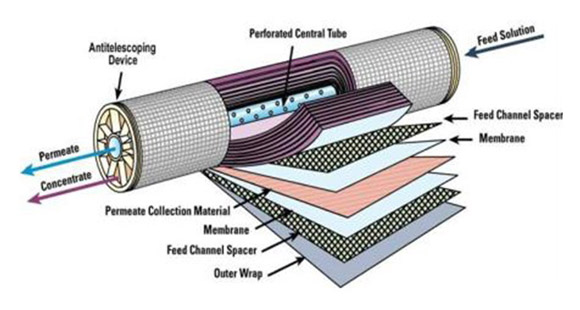
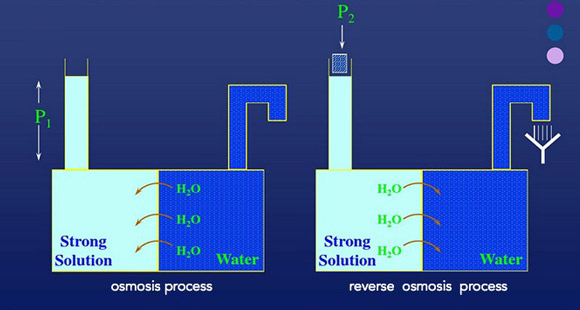
The organic membrane is a material having a selective separation function, and when there is a driving force on both sides of the membrane (such as a pressure difference, a concentration difference, a potential difference, etc.), the raw material component selectively permeates the membrane. Separation, classification, concentration and purification of different liquid or gas components can be achieved by selective separation of membranes. Since no morphological changes are required, membrane separation techniques are particularly suitable for separation processes without phase change and chemical change. Widely used in medicine, biology, food, petrochemical, energy, water treatment and other fields, resulting in huge economic and social benefits.

 English
English 한국어
한국어 français
français русский
русский Español
Español
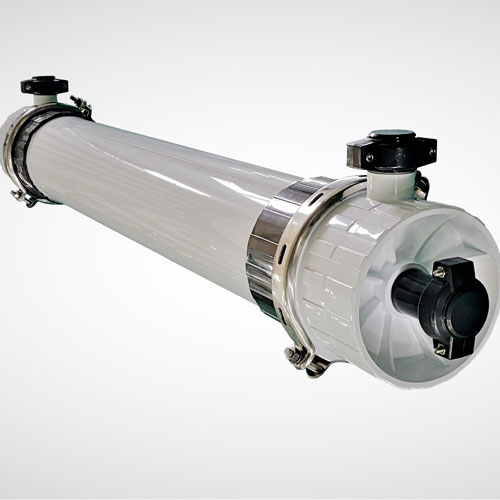
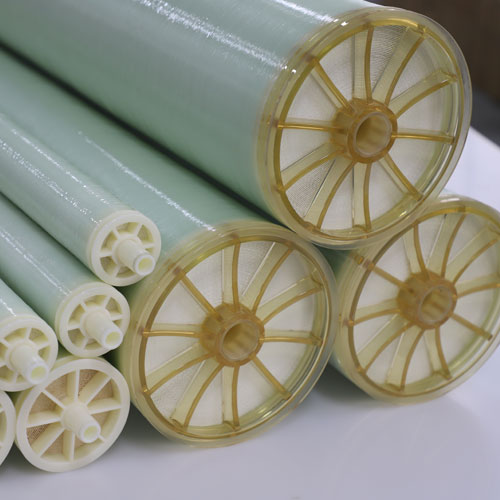
 JIUWU Organic Membrane Products
JIUWU Organic Membrane Products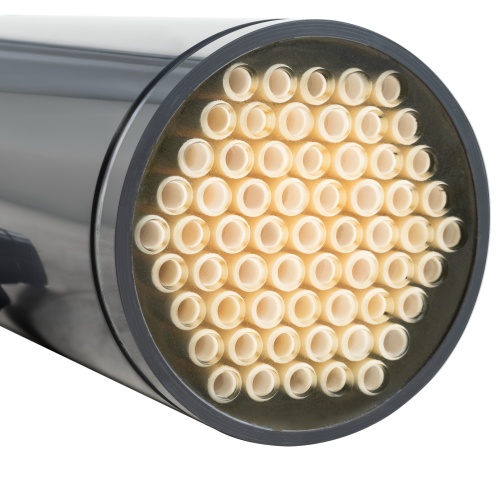 




 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  No. 9 Park Road, Pukou District, Nanjing City (Sanqiao Factory)
No. 9 Park Road, Pukou District, Nanjing City (Sanqiao Factory)
